In the world of surveying and exploration, LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) and photogrammetry have emerged as complementary technologies for generating high-quality spatial data. These methods offer efficient solutions for mapping, topographic analysis, and project planning across various industries, from mining to infrastructure development.
How Does LiDAR Work?
LiDAR operates by emitting rapid laser pulses toward a target surface and measuring the time it takes for the pulses to return. Using this time and the speed of light, LiDAR calculates the precise distance to the target. These distance measurements, combined with GPS and inertial measurement unit (IMU) data, create a detailed 3D point cloud that represents the surveyed area.
Key steps in LiDAR operation:
- Pulse Emission: A laser sends thousands of light pulses per second.
- Reflection Detection: Sensors capture the reflected pulses from surfaces such as ground, vegetation, or buildings.
- Data Processing: The system processes the returned data to create high-resolution 3D models.
How Does Photogrammetry Work?
Photogrammetry relies on overlapping images taken from different angles to recreate a 3D representation of an area. By identifying matching points in overlapping photos, the system calculates the geometry of the captured space.
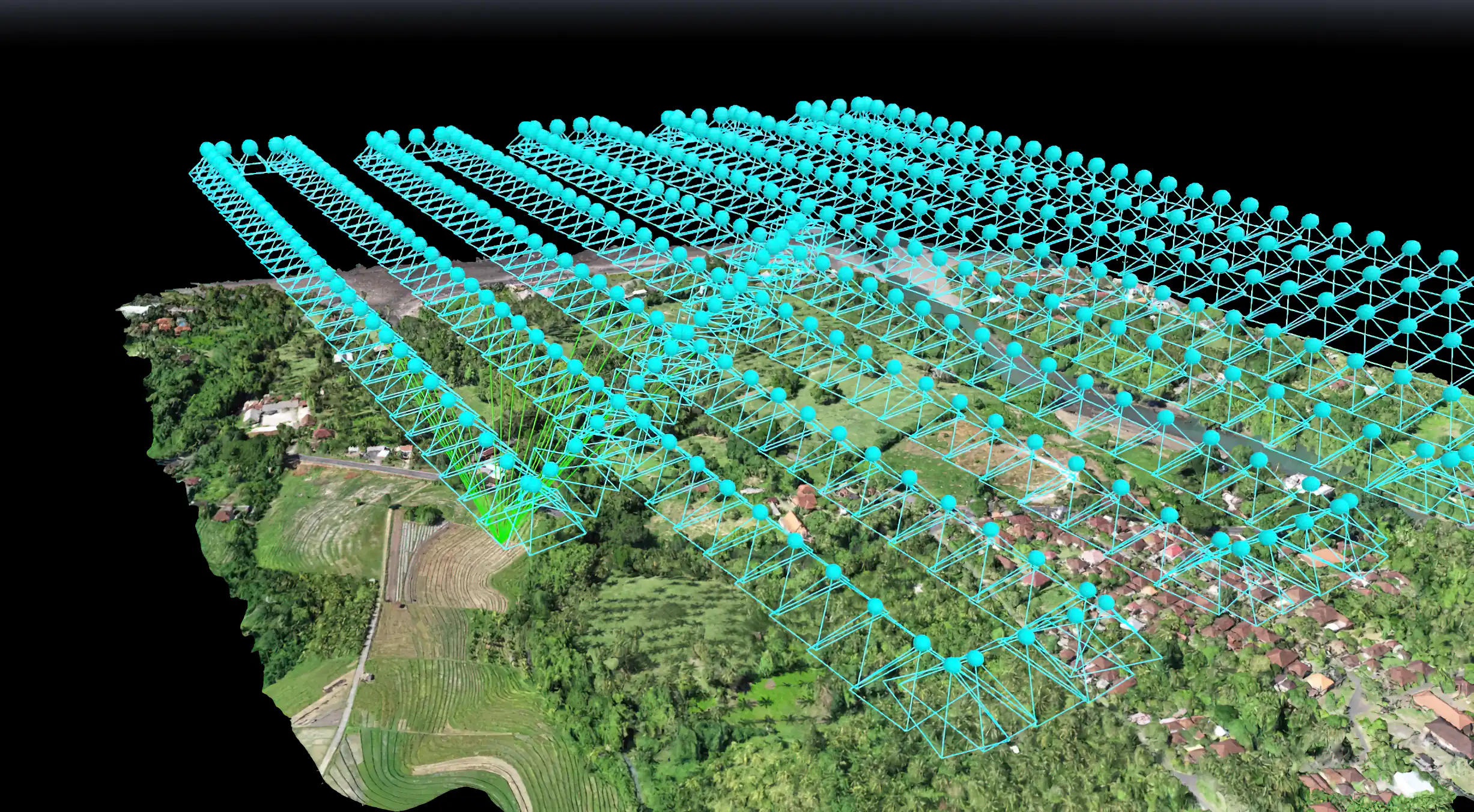
Key steps in photogrammetry operation:
- Image Capture: High-resolution images are captured using UAVs, airplanes, or ground-based cameras.
- Point Matching: Algorithms identify identical features in multiple images.
- 3D Reconstruction: The matched points are used to generate a 3D model or orthomosaic.
Advantages of LiDAR and Photogrammetry
While both methods are valuable, they serve slightly different purposes:
- LiDAR: Excels at penetrating vegetation and capturing bare-earth models, making it ideal for densely forested areas.
- Photogrammetry: Provides detailed visual textures, ideal for creating photorealistic models of structures or landscapes.
Combining LiDAR and Photogrammetry
The integration of LiDAR’s precision and photogrammetry’s visual detail results in a more comprehensive dataset. For instance:
- LiDAR data can highlight ground elevations and subsurface features.
- Photogrammetry adds texture and color to produce user-friendly 3D visualizations.
Industry Applications
- Mining: Conducting mineral exploration, designing open-pit mines, and ensuring slope stability.
- Infrastructure: Surveying construction sites, highways, and bridges.
- Environmental Studies: Monitoring land changes, evaluating flood risks, and supporting reforestation efforts.
The Future of LiDAR and Photogrammetry
As advancements in drone technology and processing software continue, LiDAR and photogrammetry are becoming increasingly accessible. Their ability to provide accurate, detailed, and efficient solutions positions them as essential tools in modern surveying and planning.
Looking to leverage LiDAR or photogrammetry for your project? Enmintech offers advanced solutions tailored to your exploration and mapping needs. Contact us today to learn more!
